Is printing ink solvent toxic? Levels of impact and how to minimize them.
14/07/2025
|
Industry news
Ink thinner solvents are now widely used in various manufacturing industries to dissolve ink and improve print quality. However, many types of solvents may contain harmful chemicals that pose risks to human health and the environment. So, is printing ink solvent toxic? What effects do they have and how can we minimize the risks? For accurate answers, let’s dive into the details of ink thinner solvents in the article below!
What Is an Ink Thinner Solvent?
An ink thinner solvent is a liquid used to dissolve, dilute, or adjust the viscosity of printing ink, making it easier to apply the ink to surfaces and ensuring the quality of printed materials. Solvents are typically selected based on the type of ink (e.g., water-based, oil-based, UV ink) and the printing technology used (offset printing, flexographic printing, inkjet printing, etc.).
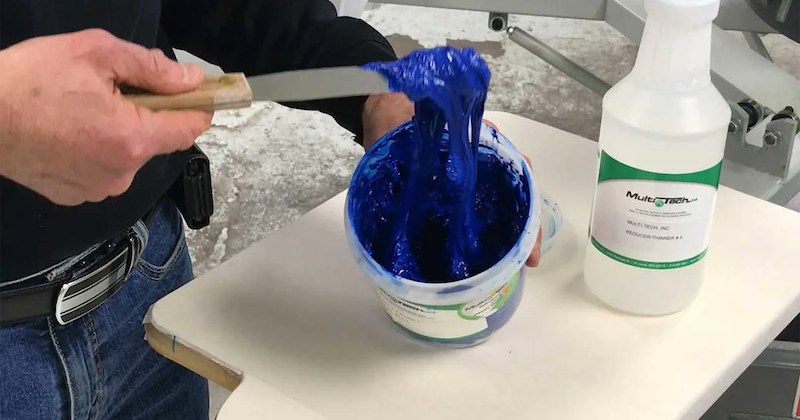

How Do Ink Thinner Solvents Affect Human Health?
Inhalation Exposure:
- Volatile solvents (such as alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters/ketones) can irritate the nose, throat, and eyes when inhaled. In more severe cases, they can cause dizziness, headaches, or nausea. Prolonged exposure to hydrocarbons (like toluene) may negatively affect the nervous system, liver, and kidneys.
- Water is generally not hazardous unless it is contaminated by other ink chemicals.
Skin Contact
- Solvents such as alcohols, esters/ketones, and hydrocarbons can dry out the skin, causing irritation or cracking with frequent exposure.
- Some solvents (like xylene) can penetrate the skin and cause systemic toxicity.
Other Risks:
- Flammable solvents (like acetone, toluene) pose fire hazards.
- If accidentally ingested, chemical solvents (alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters) can cause serious poisoning.
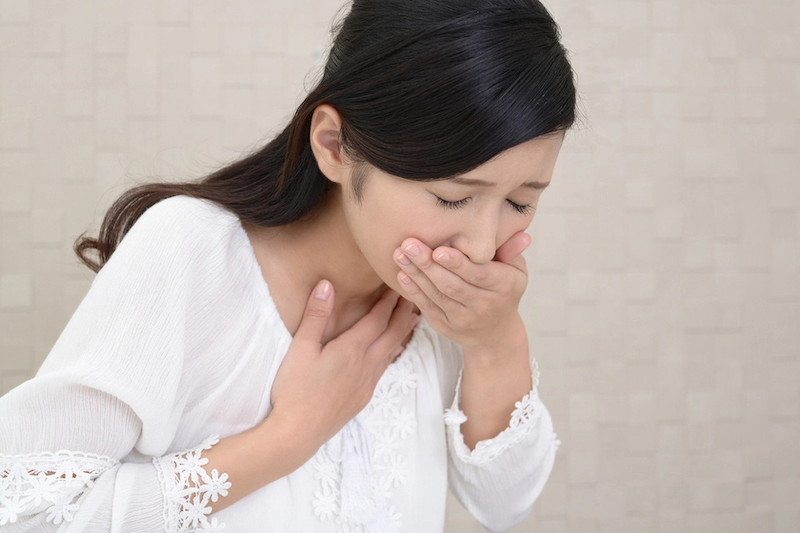

How Do Ink Thinner Solvents Affect Earth’s Health?
Air Pollution:
- Organic solvents (alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters/ketones) are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to air pollution, ground-level ozone formation, and climate change.
- Water does not contribute to air pollution.
Water Pollution:
- If chemical solvents (such as hydrocarbons or esters) are discharged into water sources without treatment, they can harm aquatic life and contaminate groundwater.
- Although wastewater from water-based inks is less toxic, it still requires treatment to remove ink residues or other chemicals.
Soil Pollution: Hydrocarbons and some esters are not easily biodegradable and can accumulate in soil, affecting ecosystems and plant growth.
5 Common Types of Ink on the Market
Powder Ink
This type of ink is commonly used in laser printers. It is made up of ultra-fine particles that vaporize quickly under high temperatures. Powder ink delivers sharp, long-lasting print quality on various paper types and is especially effective for printing high-resolution text and images.

Liquid Water-Based Ink
Mainly used in inkjet printers, this ink consists of colorants dissolved in a solvent. Thanks to its liquid form, it can be easily sprayed onto paper, creating vibrant and detailed prints. It is often used for printing images and color documents.

UV Ink
This is a special type of ink that requires UV light for curing and fixing onto the surface. UV ink dries quickly and offers high durability and print performance on many different materials. It is widely used in modern printing technologies such as advertising or packaging printing.

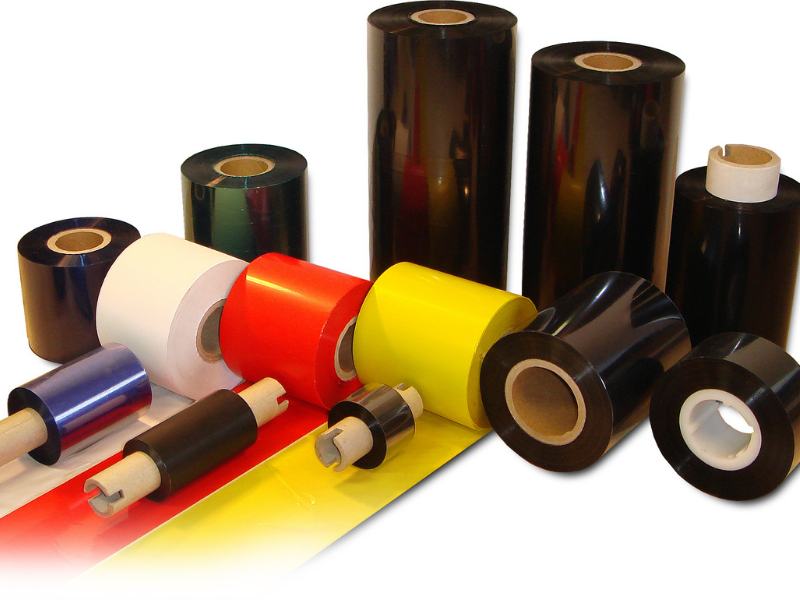
Ribbon Ink (Thermal Transfer Ribbon)
Commonly used in thermal printers, ribbon ink comes in the form of a thin roll containing a layer of ink. When heat is applied, the ink transfers from the ribbon onto the surface, forming text or images.

Thermal Paper with Integrated Ink
This type of paper has ink embedded within it, allowing for printing simply by applying heat. Thermal paper is primarily used in thermal printers and is commonly seen in receipt printers, bus ticket machines, or credit card devices.

4 Harmful Solvents Commonly Found in Printing Ink
Toluene
Toluene is a key solvent used to dissolve ink components and enhance adhesion to the printing surface. However, prolonged exposure can severely affect the nervous system, causing symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and memory loss.

Methylene Chloride
This solvent accelerates the evaporation rate of ink, allowing it to dry faster. However, frequent exposure may negatively impact the cardiovascular system, muscle strength, and motor coordination.

Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate acts as a dissolving agent and helps control the drying speed of ink. However, long-term inhalation or exposure may irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing, dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue.

Cyclohexane
This solvent enhances ink adhesion. However, cyclohexane can seriously affect the nervous system, potentially causing motor disorders and, in severe cases, coma.
Safety Measures and Risk Reduction When Using Solvents
Protecting Human Health
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
-
-
- Wear chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile or latex gloves) to avoid direct contact with solvents.
- Use respirators or protective masks especially for volatile solvents such as hydrocarbons or esters/ketones to protect your respiratory tract.
- Wear safety goggles to prevent solvent splashes from reaching your eyes.
-
- Ensure Proper Ventilation:
-
-
- Install ventilation systems or exhaust fans to reduce solvent vapor concentration in the air.
- Avoid working in enclosed spaces with volatile solvents like toluene or acetone.
-
- Training and Awareness:
-
-
- Train employees on safe handling of solvents and recognizing symptoms of overexposure (such as dizziness or irritation).
- Clearly label solvent containers with hazard warnings (toxic, flammable, etc.).
-
- Limit Exposure:
-
-
- Use tools such as pumps or tubing instead of pouring solvents by hand.
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling, and avoid prolonged skin contact with solvents.
-
- Incident Response:
-
- Keep emergency eyewash stations and first aid kits ready in case solvents come into contact with eyes or skin.
- If someone inhales excessive fumes, move them to a well-ventilated area and seek medical attention if necessary.
Measures to Minimize Environmental Impact
Choose Eco-Friendly Solvents:
- Prioritize the use of water-based solvents or bio-ethanol instead of hydrocarbons and esters/ketones to reduce VOC emissions and toxicity.
Waste Management:
- Collect used solvents in sealed, labeled containers. Avoid discharging them directly into drains or the environment.
- Recycle solvents (if possible) through distillation or send them to certified waste treatment facilities.
- Treat wastewater containing ink and solvents through filtration systems before releasing it into the environment.
Reduce VOC Emissions:
- Use printers equipped with solvent recovery systems to minimize emissions into the air.
- Keep solvent containers sealed when not in use to limit evaporation.
Comply with Legal Regulations:
- Follow local environmental and occupational safety regulations (e.g., VOC emission limits, hazardous waste handling requirements).
General Risk Prevention Measures
Fire and Explosion Prevention:
- Store flammable solvents (such as acetone and toluene) in cool, well-ventilated areas, away from heat sources, sparks, or open flames.
- Use fire-resistant containers with grounding systems to prevent static electricity buildup.
- Keep appropriate fire extinguishers (suitable for chemical fires) readily available in the workplace.
Control Usage Amounts:
- Mix only the amount of solvent needed to avoid waste and difficulty in disposal.
- Use accurate measuring equipment to minimize spills or leakage.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect printers and solvent storage systems for leaks or damage.
- Maintain ventilation and solvent recovery systems routinely.
Hopefully, this article has helped you answer the question: Are ink thinner solvents toxic? Although these solvents can negatively affect human health and the environment, by following safety measures, we can protect ourselves and contribute to a more sustainable living environment. For Consultation or Further Information, Please Contact:
K-CHEM VIETNAM CO., LTD
- Address: N6B Street, Lot F, Phu Chanh 1 Industrial Cluster, Phu Chanh Ward, Tan Uyen City, Binh Duong Province, Vietnam
- Tel: +84 274 362 0218
- Email: info@k-chem.vn






