Oil paint solvents: 3 popular types and usage guide
20/06/2025
|
Industry news
Paint solvents play a crucial role in adjusting viscosity and improving paint adhesion to surfaces. Choosing and using the right solvent not only enhances the quality of the finished paint surface but also ensures the safety of applicators during use. The following article will provide useful information about types of oil-based paint solvents, their functions, how to use them, and necessary storage considerations.
What is Oil-Based Paint Solvent?
Oil-based paint solvents are liquids used to thin oil-based paints, making them easier to apply (e.g., for brushing, spraying, or rolling), adjusting viscosity, and aiding the drying process. Solvents are typically volatile organic compounds that can dissolve the resins and oils present in the paint.
Common Types of Oil-Based Paints
- Alkyd Paint: Uses alkyd resin as a binder, common for wood, metal, and interior applications. This type offers good durability and is easy to apply.
- Polyurethane Paint (PU Paint): Uses polyurethane resin, known for high durability and good weather resistance, often used for outdoor or industrial surfaces.
- Epoxy Paint: Uses epoxy resin, boasting excellent corrosion resistance and adhesion, commonly used for workshop floors, metal, or concrete.
Key Functions of Oil-Based Paint Solvents
- Dissolving Paint: Solvents help thin oil-based paints, allowing the components within the paint to mix more easily and uniformly.
- Viscosity Adjustment: They assist in adjusting the paint’s consistency to suit different application methods, making the painting process smoother and easier.
- Aiding Evaporation: With their volatile nature, oil-based paint solvents help the paint layer dry quickly and adhere better to the surface.
- Improving Paint Adhesion: Solvents help the paint penetrate evenly into the material surface, thereby increasing the durability and color uniformity of the finished work.
Common Types of Oil-Based Paint Solvents
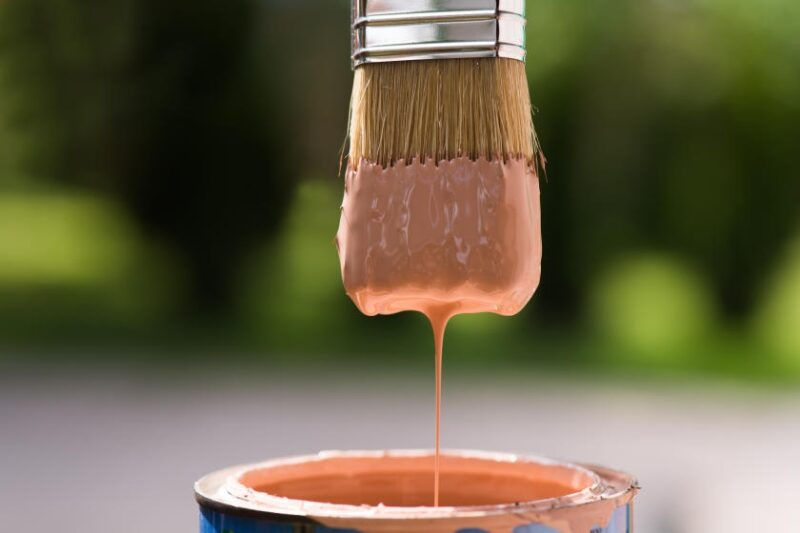
Lacquer Thinner
- Characteristics: This is the most common solvent, with a mild aromatic odor, fast evaporation, and good solvency for oil-based paints.
- Applications: Used to thin paint for hand brushing, spraying, or cleaning tools after painting (brushes, spray guns).
- Advantages: Affordable, readily available, highly effective.
- Note: There are various types of thinners (NC thinner, PU thinner, etc.), so choose the one compatible with your paint (refer to the manufacturer’s instructions).

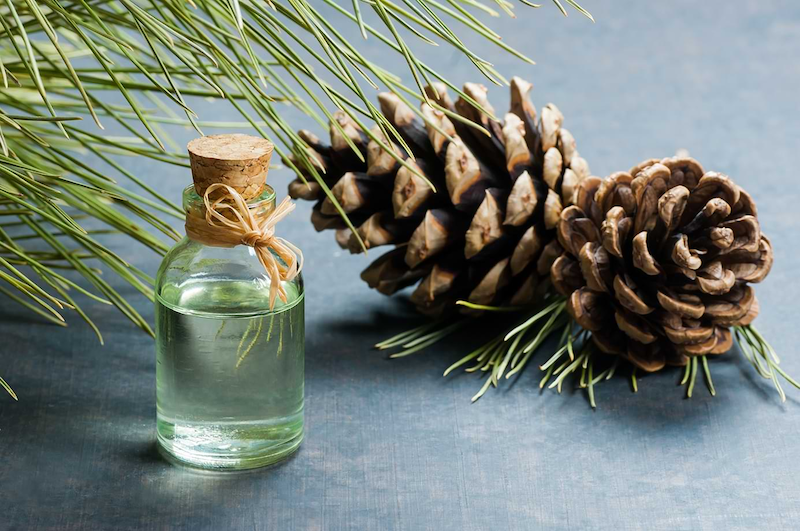
Turpentine
- Characteristics: Extracted from pine resin, it has a distinct odor and evaporates slower than lacquer thinner.
- Applications: Used to thin oil-based paints, especially for art paints or wood finishes, as it helps the paint dry evenly and retain its gloss.
- Advantages: Less harmful to health compared to some synthetic solvents, environmentally friendlier.
- Disadvantages: Higher cost, slow evaporation rate leads to longer drying times.

Mineral Spirits
- Characteristics: A hydrocarbon solvent, less odorous than lacquer thinner, with a medium evaporation rate.
- Applications: Used to thin oil-based paints for metal or wood surfaces, or for cleaning tools.
- Advantages: Less toxic than lacquer thinner, suitable for those sensitive to chemical odors.
- Disadvantages: Solvency might be lower for some specific types of paint.

Acetone (Included based on context, as the characteristics align)
- Characteristics: A strong solvent that evaporates very quickly, with a pungent odor.
- Applications: Often used for cleaning surfaces before painting or for thinning oil-based paints in some special cases (less common).
- Advantages: High cleaning effectiveness, fast drying.
- Disadvantages: Evaporates too quickly, making it not ideal for spray painting, and can cause uneven drying of the paint.

Manufacturer-Specific Solvents
- Characteristics: Some paint brands (like Dulux, Jotun, Nippon, etc.) produce their own specialized solvents, optimized for their products.
- Applications: Used to thin paint according to recommended ratios to ensure the best durability, coverage, and color.
- Advantages: Perfect compatibility with paints of the same brand, reduces the risk of paint damage.
- Disadvantages: Higher price and harder to find if not purchased with the paint.
Important Considerations for Using Oil-Based Paint Solvents
When working with oil-based paint solvents, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal results and safety.
- Compatibility Level: Not all solvents are suitable for every type of oil-based paint. Always check the manufacturer’s recommendations on the paint can to avoid damaging the paint (e.g., PU paints and alkyd paints have different requirements).
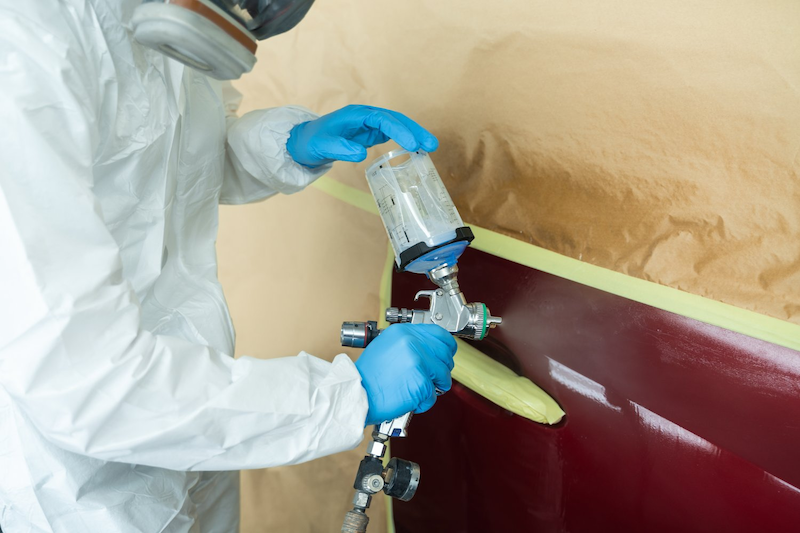
- Purpose of Use: Choose a fast-evaporating solvent (like acetone, thinner) for spray painting, or a slow-evaporating solvent (like turpentine) for brushed paint that requires a smooth finish.
How to Mix Solvents into Oil-Based Paint
Prepare Tools and Materials
- Oil-based paint: Select the appropriate paint for your purpose (wood, metal, wall paint, etc.).
- Solvent: Commonly used options include lacquer thinner, turpentine, or a specialized solvent recommended by the paint manufacturer.
- Tools: A mixing bucket or container, a stirring stick (wood or metal), a measuring cup (if precise measurement is needed), a respirator/mask, and gloves for safety.
Determine the Mixing Ratio
The ratio of solvent to oil-based paint depends on the type of paint and its intended use (primer, topcoat, spray application, or hand brushing). Generally:
- Hand brushing: Mix approximately 5-10% solvent (e.g., 100ml solvent for 1 liter of paint).
- Spray painting: Mix 20-30% solvent to thin the paint, allowing for even spraying.
Always check the manufacturer’s instructions on the paint can for the exact ratio, as each type of paint may have different requirements.
Mixing Procedure
- Step 1: Pour the oil-based paint into the mixing container first.
- Step 2: Slowly add the solvent to the paint according to the determined ratio. Do not pour paint into the solvent as this can cause the paint to clump.
- Step 3: Use the stirring stick to mix the mixture thoroughly for about 5-10 minutes until the paint and solvent are completely blended, with no cloudiness or separation.
Check Consistency
After mixing, check the paint’s viscosity:
- For hand brushing: The paint should flow smoothly, being neither too thick nor too thin.
- For spraying: The paint needs to be thin enough not to clog the spray gun nozzle, but still provide good coverage.
If adjustment is needed, add solvent or paint gradually and stir again.
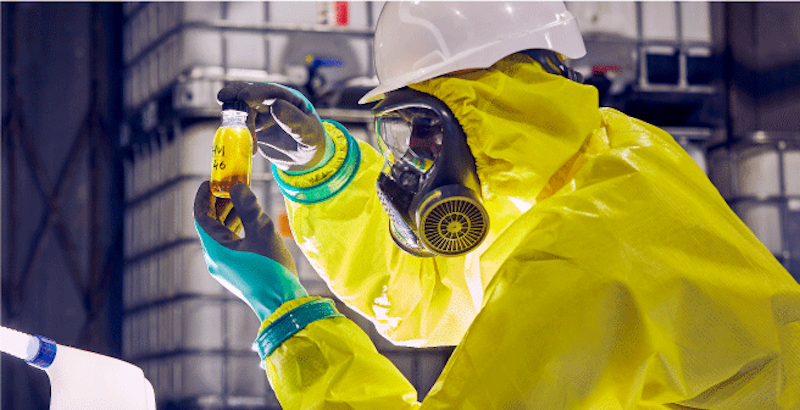
Safety Notes for Using Oil-Based Paint Solvents
Oil-based paint solvents are highly volatile, flammable, and can negatively affect health if not used correctly. To ensure safety during use, you must adhere to the following principles:
- Use solvents in dry, well-ventilated areas to limit inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Wear full protective gear (gloves, mask, safety goggles) to avoid direct skin contact.
- Absolutely do not directly sniff the solvent.
- In case of solvent contact with skin or eyes, rinse thoroughly with water immediately.

Storage Notes for Oil-Based Paint Solvents
- Work in a well-ventilated area, away from ignition sources, as both solvents and oil-based paints are highly flammable.
- Wear a mask and gloves to avoid inhaling solvent vapors or direct skin contact.
- Store the mixed paint in a sealed container, avoiding prolonged storage as the solvent can evaporate.
Oil-based paint solvents play a pivotal role in determining surface quality, drying time, and the durability of the paint layer. Each type of solvent possesses unique characteristics, suitable for specific purposes. Simultaneously, choosing the right solvent for each type of oil-based paint also helps protect the health of the applicator and minimizes negative impacts on the environment.
Businesses can leave their information or receive free consultation from our experienced team via the information below:
K-CHEM VIETNAM CO., LTD
- Address: N6B Road, Lot F, Phu Chanh 1 Industrial Cluster, Phu Chanh Ward, Tan Uyen City, Binh Duong Province, Vietnam
- Tel: +84 274 362 0218
- Email: info@k-chem.vn






